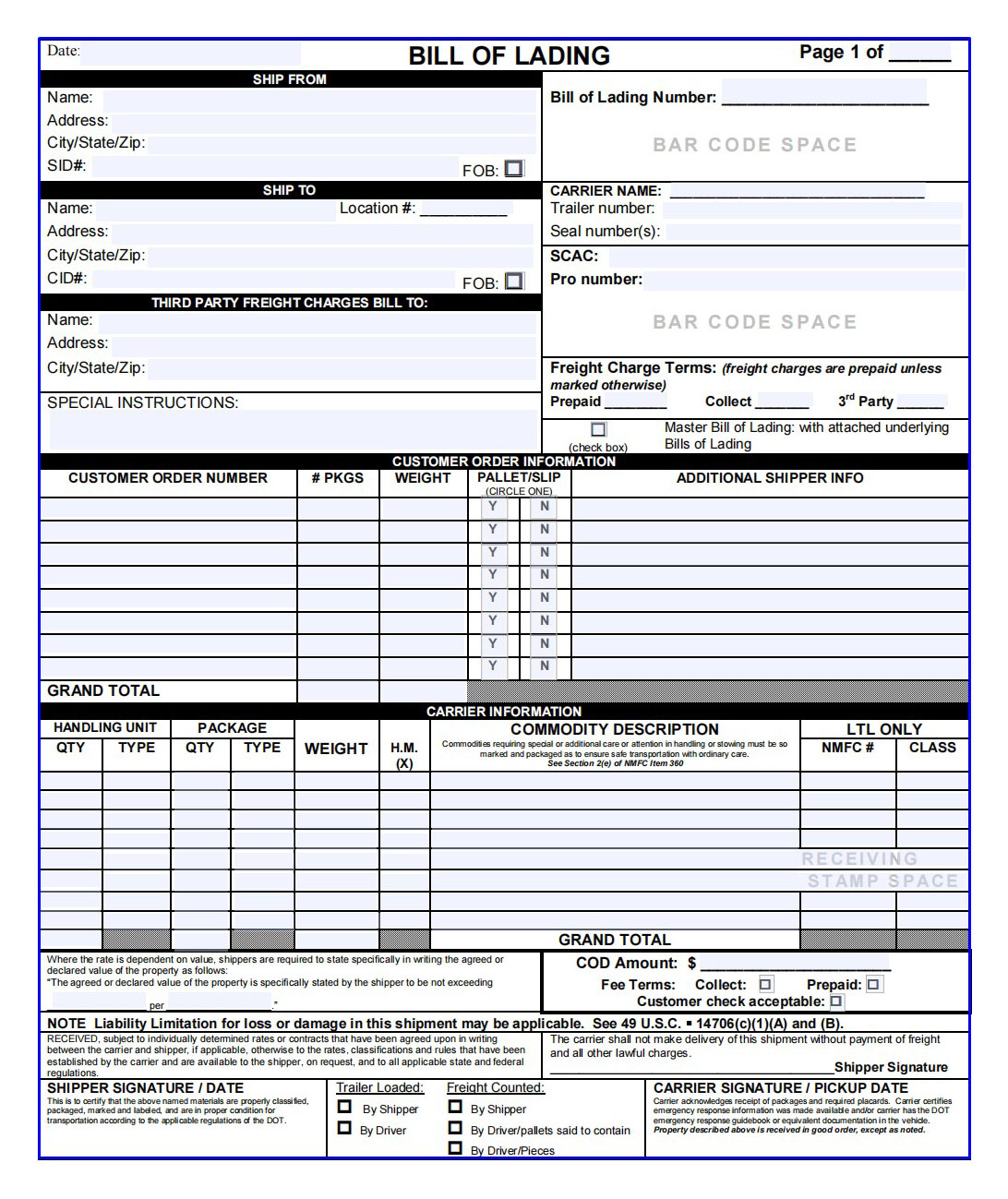
Bill of Lading
A bill of lading is an important document issued by a carrier to a shipper confirming that the goods have been received in acceptable condition and are ready to be shipped. It is a legally binding document that often serves as proof of ownership of the goods being transported, since only the consignee named on the bill of lading has the contractual rights to claim the cargo’s release.
What is the Bill of Lading used for?
The Bill of Lading (B/L or Bill of Lading) performs several important functions during export shipment:
- Evidence of concluding a contract of carriage
A bill of lading is essentially a contract of carriage between the Sender, the Consignee and the Carrier, defining the terms of carriage.
- Receipt of goods
It acts as proof of delivery, confirming that the item was received in acceptable condition and is ready to ship.
- Document of ownership of goods
The bill of lading also serves as proof of ownership of the goods being transported. The owner of the cargo (holder of the bill of lading) has the legal rights to claim the goods or arrange for the transfer of ownership of the cargo to another participant in the supply chain. In some cases, the shipper may withhold the bill of lading until payment is received from the consignee. In this case, the Consignee will not be able to access his goods until payment is made and the bill of lading is issued.
What is the difference between freight collection and freight prepayment?
The bill of lading may indicate that the cargo was sent under Freight Collect or Freight Prepaid terms. These terms refer to which party will pay international shipping costs.
If the shipment is sent by Freight Collect, the cost of transportation will be “collected” by the Consignee. If the shipment was shipped on a freight prepaid basis, the shipper will be invoiced for the freight charge.
It is important to note that the carrier must receive payment of shipping charges (either party) BEFORE releasing the shipment to the Consignee.
- Incoterms for cargo collection include – EXW, FCA, FAS, FOB.
- Incoterms for prepaid freight transport include – CFR, CIF, CPT, CIP, DAP, DPU, DDP.
What information is contained in the bill of lading?
- Shipper details, including company name, address and contact details.
- Consignee details including company name, address and contact details.
- Notification of the party (if it is not the Consignee). In most cases, the Notifying Party will be the same as the Consignee, so the Notifying Party will be labeled “same as Consignee.” This notifying party can be used to notify any 3 parties that need to be informed about the updates, progress and delivery of the shipment.
- Carrier information, including company name, logo, address, contact information and terms of carriage.
- Bill of lading number – a unique bill of lading number issued by the transport company or forwarder organizing the transportation of goods.
- Vessel name and voyage number
- Receipt location, Loading port, Discharge port, Delivery location, Final destination
- Container number, seal number, transport signs and numbers, product description, gross weight, volume, special instructions.
- Prepayment for freight or freight fee
- Place and date of issue, signature

