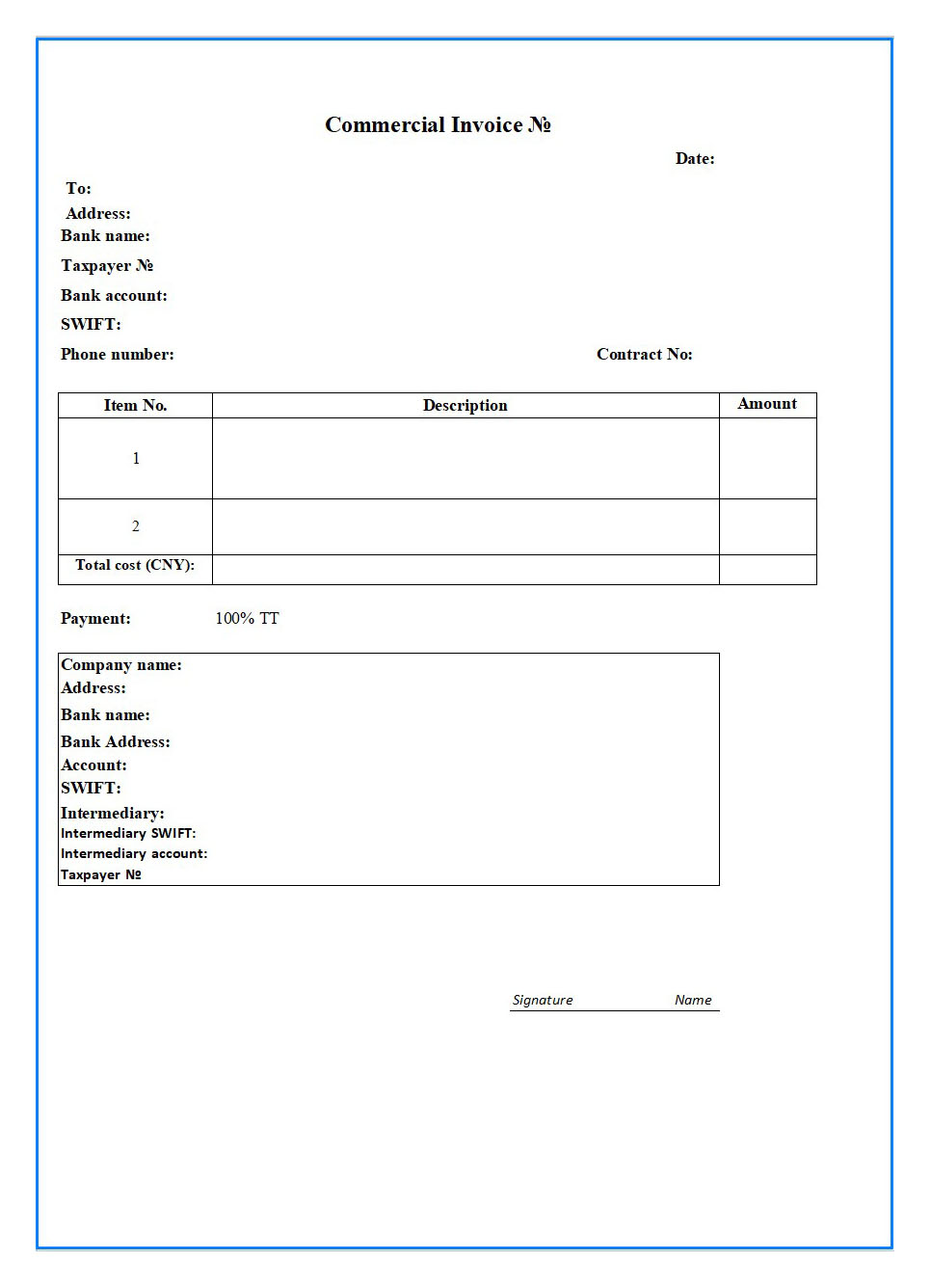
Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice is one of the most important documents in trading, detailing things such as the description and value of the goods being shipped, as well as shipper information. It is commonly used by customs authorities to assess applicable taxes and duties.
What is a commercial invoice used for?
A commercial invoice is required for all sea, rail and air shipments. When products are shipped overseas, the exporter will need to create a commercial invoice along with shipping documentation to provide it to the importer to arrange customs clearance, and in cases where a letter of credit has been used for payment, the importer will provide the commercial invoice to their bank to initiate the release funds.
Customs authorities rely on the description and the value of the goods shown on the commercial invoice to determine applicable taxes and duties, so it is important that the commercial invoice contains all the necessary information to avoid importers encountering any problems or delays in clearing goods through customs.
What is the difference between a Proforma Invoice and a Commercial Invoice?
These two documents are essentially the same, however, sometimes the quantity of goods shown on the commercial invoice may differ from the quantity of goods shown on the proforma invoice. This is because the quantity of goods ordered (from the proforma invoice) may differ from the actual quantity of goods shipped (from the commercial invoice).
This difference can be caused by many reasons, but the most common ones are that the supplier experienced production problems or delays, or that the supplier did not properly plan how many products would fit into the shipping containers. It is because of this discrepancy that a commercial invoice is typically issued upon delivery or shipment of goods to ensure that it accurately reflects the final quantity of goods shipped.
What information is contained in a commercial invoice?
- Seller details – company name, address and contact information.
- Buyer details – company name, address and contact information.
- Dispatch method – road, rail, air or sea transport.
- Type of transportation – FCL, LCL, bulk shipments or other.
- Loading port and unloading port – seaport, railway station or airport.
- Reference number & date
- Date of delivery
- Terms and payment method
- Product Descriptions – Including product codes/items, product descriptions, number of units, unit type and price.
- Incoterms – agreed terms of sale
- Bank details – the bank account into which you want the buyer to make the payment.
- Name, date and signature of the company’s authorized representative

